Abstract
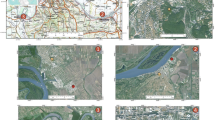
The aim of this research was to quantify the content of hazardous elements in the needles of Norway spruce (Picea abies L.) in the natural habitats that were accumulated from thermal power plants, mines, and metal processing industry. Fifteen natural populations of the Norway spruce were sampled from the mountain ranges in Southeastern Europe (Dinaric Alps and Balkan Mountains). Two-year-old spruce needles were evaluated the content of the following hazardous elements: heavy metals cadmium, mercury, nickel, lead and zinc, and metalloid arsenic. The effect of the distance between air pollution emitters and the Norway spruce natural habitats on the hazardous elements content in needles was also evaluated. The results of the analysis of variance confirmed interpopulation differences in the content of all analyzed hazardous elements. The effect of the air pollution source (thermal power plants, mines, and industry) on the content of hazardous elements in the spruce needles was also assessed. Significant correlation was found between the distance of air pollution emitters and the amount of zinc. This study could serve as the startup point of future monitoring programs and provide new prospect of using Norway spruce needles as the bioindicator of air pollution with hazardous elements on Balkan Peninsula since the fact that the Norway spruce natural populations inhabit wide geographic range of the continental Europe, from the Balkan Peninsula, over European Alps to Scandinavia and a large-scale of altitude from 980 to 1860 m above sea level.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Alexandrino, K., Viteri, F., Rybarczyk, Y., Guevara Andino, J. E., & Zalakeviciute, R. (2020). Biomonitoring of metal levels in urban areas with different vehicular traffic intensity by using araucaria heterophylla needles. Ecological Indicators, 117, 106701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106701
Al-Khashman, O. A., Al-Muhtaseb, A. H., & Ibrahim, K. A. (2011). Date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) leaves as biomonitors of atmospheric metal pollution in arid and semi-arid environments. Environmental Pollution, 159(6), 1635–1640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.02.045
Briffa, J., Sinagra, E., & Blundell, R. (2020). Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon, 6(9), e04691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04691
Čeburnis, D., & Steinnes, E. (2000). Conifer needles as biomonitors of atmospheric heavy metal deposition: Comparison with mosses and precipitation, role of the canopy. Atmospheric Environment, 34(25), 4265–4271.
De La Cruz, A., Ferreira, L., Andrade, V., & Gioda, A. (2019). Biomonitoring of toxic elements in plants collected near leather tanning industry. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 30, 256–264. https://doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20180174
Dogan, Y., Unver, M. C., Ugulu, I., Calis, M., & Durkan, N. (2014). Heavy metal accumulation in the bark and leaves of Juglans regia planted in Artvin city, Turkey. Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment, 28(4), 643–649. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2014.947076
EEA, (2014). Exposure of ecosystems to acidification, eutrophication and ozone (Indicator CSI 005), European Environment Agency
Giordano, S., Spagnuolo, V., & Capozzi, F. (2021). Biomonitoring of Air Pollution. Atmosphere, 12(4), 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12040433
Goczał, J., Oleksa, A., Rossa, R., Chybicki, I., Meyza, K., Plewa, R., Landvik, M., Gobbi, M., Hoch, G., Tamutis, V., Balalaikins, M., Telnov, D., Dascălu, M., & Tofilski, A. (2020). Climatic oscillations in quaternary have shaped the co-evolutionary patterns between the Norway spruce and its host-associated herbivore. Scientific Reports, 10(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-73272-0
Guerreiro, C. B., Foltescu, V., & De Leeuw, F. (2014). Air quality status and trends in Europe. Atmospheric Environment, 98, 376–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.09.017
Hamann, A., Wang, T., Spittlehouse, D. L., & Murdock, T. Q. (2013). A comprehensive, high-resolution database of historical and projected climate surfaces for western North America. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 94(9), 1307–1309. https://doi.org/10.1175/bams-d-12-00145.1
Hoodaji, M., Ataabadi, M., & Najafi, P. (2012). Biomonitoring of airborne heavy metal contamination. Air Pollution - Monitoring, Modelling, Health and Control. 21, https://doi.org/10.5772/32963
Kandziora-Ciupa, M., Ciepał, R., Nadgórska-Socha, A., & Barczyk, G. (2016). Accumulation of heavy metals and antioxidant responses in Pinus sylvestris L. needles in polluted and non-polluted sites. Ecotoxicology, 25(5), 970–981. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1654-6
Knežević, M., Belanović, S., Košanin, O., & Kadović, R. (2000). Sadržaj teških metala u šumi bukve na Crnom vrhu i kitnjaka na Fruškoj gori. Acta Biologica Iugoslavica-Serija a: Zemljište i Biljka, 49, 19–28.
Ippolitova, N. A. (2019). Anthropogenic impact of industrial production on the environment (on the example of the Siberian region). In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science (Vol. 381, No. 1, p. 012035). IOP Publishing.
Lin, Y., & Aarts, M. G. (2012). The molecular mechanism of zinc and cadmium stress response in plants. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 69(19), 3187–3206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1089-z
Lodenius, M. (2013). Use of plants for biomonitoring of airborne mercury in contaminated areas. Environmental Research, 125, 113–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2012.10.014
Lüttge, U., & Buckeridge, M. (2020). Trees: Structure and function and the challenges of urbanization. Trees, 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-020-01964-1
Madejón, P., Marañón, T., Murillo, J. M., & Robinson, B. (2004). White poplar (Populus alba) as a biomonitor of trace elements in contaminated riparian forests. Environmental Pollution, 132(1), 145–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.03.015
Mancheno, T., Zalakeviciute, R., González-Rodríguez, M., & Alexandrino, K. (2021). Assessment of metals in PM10 filters and Araucaria heterophylla needles in two areas of Quito, Ecuador. Heliyon, 7(1), e05966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e05966
Marković, D. M., Milošević, I. R., & Vilotić, D. (2012). Accumulation of Mn and PB in Linden (Tilia platyphyllos scop.) bark and wood. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(1), 136–145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1024-8
Marković, D. M., Novović, I., Vilotić, D., & Ignjatović, L. (2008). Determination of as in tree-rings of poplar (Populus alba L.) by U-shaped DC arc. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 151(1–4), 377–382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0279-5
Marković, D. M., Novović, I., Vilotić, D., & Ignjatović, L. (2007). Determination of Fe, Hg, Mn, and Pb in three-rings of poplar (Populus alba L.) by U-shaped DC arc. Russian Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 81(9), 1493–1496. https://doi.org/10.1134/s0036024407090282
Matin, G., Kargar, N., & Buyukisik, H. B. (2016). Bio-monitoring of cadmium, lead, arsenic and mercury in industrial districts of Izmir, Turkey by using honey bees, propolis and pine tree leaves. Ecological Engineering, 90, 331–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.01.035
Miljković, D., Avramov, S., Vujić, V., Rubinjoni, L., Klisarić, B., Živković, U., & Tarasjev, A. (2014). Lead and nickel accumulation in Iris pumila: Consideration of its usefulness as a potential bioindicator in the natural protected area of Deliblato sands, Serbia. Archives of Biological Sciences, 66(1), 331–336. https://doi.org/10.2298/abs1401331m
Naderizadeh, Z., Khademi, H., & Ayoubi, S. (2016). Biomonitoring of atmospheric heavy metals pollution using dust deposited on date palm leaves in southwestern Iran. Atmósfera. 29(2), 141–155 https://doi.org/10.20937/atm.2016.29.02.04
Nikolić, D., Milošević, N., Živković, Z., Mihajlović, I., Kovačević, R., & Petrović, N. (2011). Multi-criteria analysis of soil pollution by heavy metals in the vicinity of the copper smelting plant in Bor (Serbia). Journal of the Serbian Chemical Society, 76(4), 625–641. https://doi.org/10.2298/jsc100823054n
Onder, S., & Dursun, S. (2006). Air borne heavy metal pollution of Cedrus libani (A. Rich.) in the city centre of Konya (Turkey). Atmospheric Environment, 40(6), 1122–1133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.11.006
Pająk, M., Gąsiorek, M., Cygan, A., & Wanic, T. (2015). Concentrations of Cd, Pb and Zn in the top layer of soil and needles of scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.): A case study of two extremely different conditions of the forest environment in Poland. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 24(1), 71–76.
Parzych, A., Mochnacký, S., Sobisz, Z., Polláková, N., & Šimanský, V. (2018). Needles and bark of Picea abies (L.) H. Karst and Picea omorika (Pančić) Purk. as bioindicators of environmental quality. Folia Forestalia Polonica, 60(4), 230–240. https://doi.org/10.2478/ffp-2018-0024
Popović, V., Nikolić, B., Lučić, A., Rakonjac, L., Šešlija Jovanović, D., & Miljković, D. (2022). Morpho-anatomical trait variability of the Norway spruce (Picea abies (L.) Karst.) needles in natural populations along elevational diversity gradient. Trees. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-022-02277-1
Rautio, P., Fürst, A., Stefan, K., Raitio, H., & Bartels, U. (2016). Manual on methods and criteria for harmonized sampling, assessment, monitoring and analysis of the effects of air pollution on forests: Part XII Sampling and analysis of needles and leaves. https://www.icp-forests.org/pdf/manual/2016/ICP_Manual_2017_01_part12.pdf
Rhind, S. M. (2009). Anthropogenic pollutants: A threat to ecosystem sustainability? Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 364(1534), 3391–3401. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2009.0122
SAS Institute Inc. (2011). The SAS system for Windows, release 9.3., SAS Inst., Cary, NC.
Sawidis, T., Breuste, J., Mitrovic, M., Pavlovic, P., & Tsigaridas, K. (2011). Trees as bioindicator of heavy metal pollution in three European cities. Environmental Pollution, 159(12), 3560–3570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.08.008
Serbula, S. M., Radojević, A. A., Kalinović, J. V., & Kalinović, T. S. (2014). Indication of airborne pollution by birch and spruce in the vicinity of copper smelter. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21(19), 11510–11520. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3120-4
Sharma, P., Kumar, S., Garg, A., & Ghosh, C. (2015). Analyzing the effect of atmospheric trace elements on selected plant species. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74(12), 7793–7800. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4452-1
Šijačić-Nikolić, M., Stanković, D., Krstić, B., Vilotić, D., & Ivetić, V. (2012). The potential of different lime tree (Tilia spp) genotypes for phytoextraction of heavy metals. Genetika, 44(3), 537–548. https://doi.org/10.2298/gensr1203537s
Stanković, D., Igić, R., Sijačić-Nikolić, M., Vilotić, D., & Pajević, S. (2009a). Contents of the heavy metals nickel and lead in leaves of Paulownia elongata S.Y. Hu and Paulownia fortunei hems. in Serbia. Archives of Biological Sciences, 61(4), 827–834. https://doi.org/10.2298/abs0904827s
Stanković, D., Krstić, B., Orlović, S., Trivan, G., Poljak, L. P., & Nikolić, M. S. (2011a). Woody plants and herbs as bioindicators of the current condition of the natural environment in Serbia. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research, 5(15), 3507–3511.
Stanković, D., Krstić, B., Sijačić-Nikolić, M., & Knezević, M. (2011b). Concentrations of manganese and iron in some Woody and herbs plants. Zbornik Matice Srpske Za Prirodne Nauke, 121, 39–49. https://doi.org/10.2298/zmspn1121039s
Stanković, D., Nikolić, M., Krstić, B., & Vilotić, D. (2009b). Heavy metals in the leaves of tree species Paulownia Elongata S.Y.Hu in the region of the city of Belgrade. Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment, 23(3), 1330–1336. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2009.10817664
Stojnić, S., V. Avramidou, E., Fussi, B., Westergren, M., Orlović, S., Matović, B., Trudić, B., Kraigher, H., A. Aravanopoulos, F., & Konnert, M. (2019). Assessment of genetic diversity and population genetic structure of Norway spruce (Picea abies (L.) Karsten) at its southern lineage in Europe. Implications for conservation of forest genetic resources. Forests, 10(3), 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10030258
Tanase, C., Nisca, A., & Lopez, A. (2021). Assessment of heavy metal content in tree barks: Picea abies, Pinus sylvestris, and Pinus nigra (Retracted). BioResources, 16(3), 5047–5057. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.16.3.5047-5057
Turkyilmaz, A., Sevik, H., & Cetin, M. (2018). The use of perennial needles as biomonitors for recently accumulated heavy metals. Landscape and Ecological Engineering, 14(1), 115–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11355-017-0335-9
Zeiner, M., & Juranović Cindrić, I. (2021). Accumulation of major, minor and trace elements in pine needles (Pinus nigra) in Vienna (Austria). Molecules, 26(11), 3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113318
Funding
This study was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia, grant numbers 451–03-68/2022–14/ 200027 and contract number 451–03-68/2022–14/ 200007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived the idea and designed the study: D.M. and V.P. Conducted fieldwork, conceptualization, and investigation: V.P. Substantive translation and correction of the final version of the manuscript: D.Š.J. Heavy metal screening via ICP-OES spectrometer: Z.M. Contribution to the draft version of manuscript: J.M. Project management responsibility for research, project administration, and funding acquisition: A.L., LJ.R., D.Š.J., and D.M. Methodology, validation, supervision, performed statistical analyses, data curation, visualization results, and writing-original manuscript: D.M.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Popović, V., Šešlija Jovanović, D., Miletić, Z. et al. The evaluation of hazardous element content in the needles of the Norway spruce (Picea abies L.) that originated from anthropogenic activities in the vicinity of the native habitats. Environ Monit Assess 195, 109 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10732-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10732-2